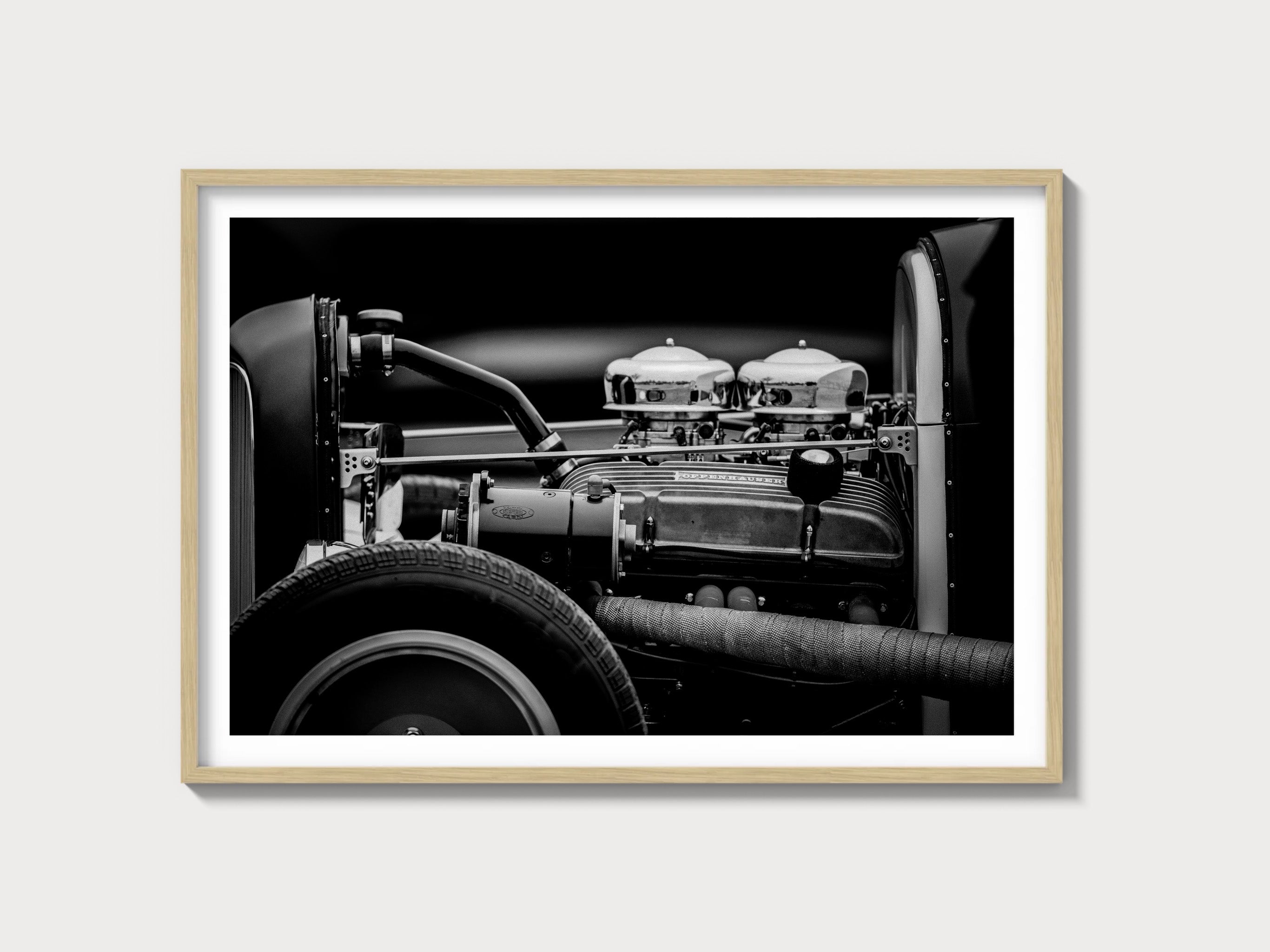
Unveiling the 1908–1927 Ford Model T Base
Historical Context and Development Background
The Ford Model T, introduced by the visionary Henry Ford in 1908, was a monumental leap in automotive manufacturing and design. It marked the advent of the assembly line in automobile production, drastically reducing costs and making car ownership a reality for the average American. This era-defining vehicle emerged during a time when competitors like the Oldsmobile Curved Dash and the Cadillac Model B were vying for market supremacy. Unlike its contemporaries, the Model T's robust design and affordability set it apart, securing its place as the best-selling car globally until the Volkswagen Beetle in the latter half of the 20th century.
Engine and Technical Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Engine Configuration | Inline 4-cylinder |
| Displacement | 177 cu in (2.9 L) |
| Horsepower | 20 HP |
| Induction Type | Natural aspiration |
| Redline | 1600 RPM |
| Fuel System | Thermo-syphon |
| Compression Ratio | 4.5:1 |
| Bore x Stroke | 3.75 in x 4.00 in |
Driving Experience and Handling Dynamics
Driving a Model T is an experience unlike any modern vehicle. The steering is direct, courtesy of a unique planetary gear system, while the suspension, featuring transverse leaf springs, provides a rudimentary yet effective ride quality. The gearbox consists of a two-speed planetary transmission, which, although archaic by today's standards, was revolutionary for offering ease of use with its three-pedal system. Throttle response is controlled via a hand lever on the steering wheel, requiring a completely different approach to driving.
Full Performance Specifications
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| 0–60 mph | Not Applicable |
| Top Speed | 45 mph |
| Quarter-Mile | Not Applicable |
| Weight | 1200 lbs |
| Layout | FR (Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive) |
| Brakes | Mechanical, rear only |
| Suspension | Transverse leaf springs |
| Gearbox Type | 2-speed planetary |
Variant Breakdown
- Touring Car: Most popular variant, open-top, produced in the millions.
- Runabout: Two-seat variant, slightly lighter, favored by young drivers.
- Coupé: Enclosed version, offering more comfort and protection from the elements.
Ownership Notes
Owning a Model T today involves understanding its unique maintenance needs. Parts are surprisingly available due to the sheer volume produced, but restoration can be labor-intensive given the car's age. Regular servicing, primarily lubrication and periodic engine checks, is essential to keep these vehicles in running order.
Cultural Relevance
The Model T has left an indelible mark on popular culture, appearing in countless films and serving as a symbol of the early 20th-century American dream. Its desirability among collectors remains high, with pristine examples fetching substantial figures at auction. The Model T's racing legacy, though not as pronounced as its road-going achievements, includes participation in early endurance events, showcasing its reliability.
FAQs
- How reliable is the Model T? Despite its age, the Model T is known for its simplicity and durability, provided it is well-maintained.
- What are the known problems of the Model T? Common issues include ignition system weaknesses and frequent need for brake adjustments.
- How has the value of the Model T trended over time? Values have generally increased as the car's historical significance has grown, with well-preserved examples commanding a premium.